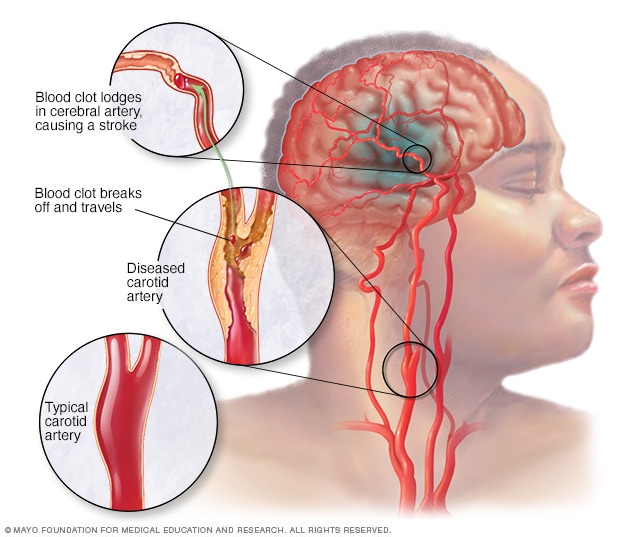
A stroke is a life-altering health emergency where immediate action is essential. It can manifest in two ways: a blockage (ischemic) or a burst (hemorrhagic) in the blood supply. The former is more common, but they are both equally dangerous.
A person with a stroke may have problems with communication, vision, and/or bodily control. They may also experience numbness on one side of the body and extreme headaches. As soon as these symptoms are noticed, it is crucial to call 911 immediately. Take note of the time the stroke started, as it could help first responders develop the necessary course of action. If the person loses their pulse, perform CPR (steps of CPR will be available at the end of this article). Under no circumstances should the patient be moved or given food, water, or medicine as it could worsen their condition.
The consequences of a stroke can last a lifetime. From paralysis to memory loss to cognitive deficits, the impacts of a stroke are devastating. Though speech and physical therapy can help, a person’s life will never be the same. The best thing a person can do is reduce their risk factors of having a stroke, which can be done by changing lifestyle choices: quitting smoking, performing more physical exercise, eating a well-balanced diet, etc.
Steps to Performing CPR
After first checking the site for potential environmental dangers, affirming the unresponsiveness of the patient, and calling 911, the following steps should be taken:
- Place the patient on flat ground. If possible, send someone to retrieve an AED.
- Interlock hands (palm to the back of the hand) and place the heel of the frontward hand on the patient’s chest.
- Give 30 chest compressions with a depth of at least 2 inches at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute (or the beat of “Staying Alive”). The chest should rise after every compression.
- Tilt the patient’s chin up, pinch the nose, and give 2 one-second breaths.
- Repeat steps 3 and 4 until help arrives.
Sources
General Overview of a Stroke: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/stroke/symptoms-causes/syc-20350113
Actions to Take When Someone Has a Stroke: https://www.pennmedicine.org/updates/blogs/neuroscience-blog/2022/march/what-to-do-if-someone-is-having-a-stroke
Steps for CPR: https://www.redcross.org/take-a-class/cpr/performing-cpr/cpr-steps